ACETIC
ACID
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
64-19-7, 77671-22-8
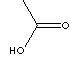
60.05
H.S. CODE
UN NO.
CLASSIFICATION
Solvent, Acetic acid
EXTRA NOTES
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
MELTING POINT
16.6 C
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
http://www.biology-online.org/
Acetic acid (Science: chemical) The acid most commonly associated with vinegar, it is the most commercially important organic acid and is
used to manufacture a wide range of
chemical products, such as plastics and acetobacter but, except for making vinegar, is usually made through synthetic processes. derivatives of
acetic acid which may be formed by substitution reactions. Mono- and di-substituted, as well as, halogenated compounds have been
synthesised. Experimentally, alpha- and n2- substituted acetic acids have been examined for their anti-inflammatory activity and effect on the central nervous system
respectively. Additionally, limited exposure data has been collected on dibromo and
dichloroacetic acids to determine whether they pose health effects. Synonym: ethanoic
Acid. A colorless pungent liquid widely used in manufacturing
plastics and pharmaceuticals.A
transparent liquid that is part of
vinegar, that gives it its characteristic smell.
http://www.cosmeticsinfo.org/
Acetic Acid:
What is it? Acetic Acid is an organic acid formed when ethanol is fermented. Vinegar is
typically a 5% solution of Acetic Acid. Brown Rice Vinegar is the vinegar
produced by the fermentation of unpolished brown rice. Natural Vinegars also
contain also contain small amounts of tartaric acid, citric acid and other
acids.
In cosmetics and personal care products, Acetic Acid, Vinegar and
Brown Rice Vinegar are used in the formulation of hair conditioners, shampoos,
hair rinses, wave sets and other hair care products. Acetic Acid is also used in
mouthwashes and breath fresheners and Vinegar can be found in skin care
products.
Local: Acetic acid is the simplest carboxylic acid next to formic acid in which a single hydrogen atom is attached to the carboxyl group. If a methyl group is attached to the carboxyl group, the compound is acetic acid. Acetic acid is a clear, corrosive, flammable liquid; melting point 16.6 C, boiling point 118 C. Pure acetic acid freezes in ice-like crystal form. So pure acetic acid is called glacial acetic acid, which contains 99.5 -100.5 % w/w. It is the two-carbon carboxylic acid, and a systematic name is ethanoic acid. It is completely miscible with water, ethyl alcohol and ether, but is insoluble in carbon disulfide. It is a characteristic component of vinegar and an important biochemical intermediate in the form of acetylcoenzyme A, mostly. Most commercial production of virgin synthetic acetic acid is based on methanol carbonylation. Significant volumes of acetic acid are recovered in cellulose acetate operations and lesser quantities during production of polyvinyl alcohol and butyral, peracetic acid, ethylene-vinyl alcohol and acetaminophen and aspirin. Capacity utilization is likely to remain high for the next few years because of good demand for purified terephthalic acid and vinyl acetate monomer.
Vinyl acetate monomer
The largest consumption of acetic acid is as a raw material to produce vinyl acetate by reaction with ethylene and oxygen or with acetylene in the presence of palladium catalyst. Vinyl acetate is polymerized to polyvinyl acetate by itself and to other copolymers with other monomers. Acetate polymers are important resins used in paints, adhesives, plastics and textile finishes.
Acetic anhydride
The next largest consumption of acetic acid is to produce acetic anhydride by condensation reaction of two acetic acid molecules. This chemical is principally used in the manufacture of cellulose acetate having the application as a base for magnetic tape and in the manufacture of textile fibres. Also, it is heated with salicylic acid to produce acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin). It is also used in the manufacture of pigments, dyes, cellulose and pesticides etc.
Solvent
Acetic acid is used as a solvent in the production of terephthalic acid from p-xylene. Terephthalic acid is the raw material for polyester fiber. Terephthalic acid has become a more important raw material for non-fiber field, PET-bottle, PET-film and engineering plastics and as poultry feed additives.
Esters
Considerable quantities of acetic acid are used to manufacture esters such as ethyl and butyl acetate. Acetate esters demonstrate good solvency for many natural and synthetic resins. They are general purpose solvents which are applied commonly in lacquer thinners, wood lacquers and a wide variety of coatings, plasticizer and pharmaceutical fields.
Chloroacetic acid
The stronger acid (chloroacetic acid) is manufactured from acetic acid by reaction with chlorine. Chloroacetic acid reacts with alkali cellulose to produce carboxymethylcellulose (CMC). Chloroacetic acid is the parent material for the production of a series of phenoxy herbicides such as 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid.
Acetic acid is used as an acidulant in a wide range of applications from eletroplating to textiles finishing operation. It is used in the manufacture of materials used in the pharmaceuticals, foods, cosmetics and colorant chemical fields including sorbic acid, dyestuffs and pigments, vitamins, antibiotics, rubber chemicals and flavor & fragrance.
APPEARANCE
Clear liquid, free from matter in suspension
99.85% min
COLOR, HAZEN
5 max
CRYSTALLISING POINT
16.35 C min.
DENSITY
1.048 - 1.051 kg/l at 20 C
NON-VOLATILE MATTER
0.003% max
CHLORIDES
1ppm max
SULFATES
1ppm max
Fe
0.5ppm max
HEAVY METALS
5ppm max
ALDEHYDES
5ppm max
FORMIC ACID
0.05% max
DISTILLATION RANGE
117.5 - 118.5 C
MOISTURE
0.15% max
TRANSPORTATION
2789
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLVENTS
|
Polarity |
Group |
Formula |
|
Polar |
Water |
H-OH |
|
↑ |
Carboxylic Acids |
R-COOH |
|
↑ |
Amides |
R-CONH2 |
|
↑ |
Alcohols |
R-OH |
|
↑ |
Amines |
R-NH2 |
|
↑ |
Ketones (Aldehydes) |
R-CO-R' |
|
↑ |
Esters |
R-COOR' |
|
↑ |
Alkyl Halides |
R-X |
|
↑ |
Ethers |
R-O-R' |
|
↑ |
Aromatics |
Ar-H |
|
Non-polar |
Alkanes |
R-H |
| Solvent |
CAS RN |
Formula | M.W. | Boiling Point (°C) | Melting Point (°C) | Density | Solubility in water (g/100g) | Dielectric Constant | Flash Point (°C) |
| Acetic Acid | 64-19-7 | C2H4O2 | 60.05 | 118 | 16.6 | 1.049 | Miscible | 6.15 | 39 |
|
Acetic Anhydride |
108-24-7 | C4H6O3 | 102.09 |
138-140 |
-73.1 | 1.08 | 12 |
- | 54 |
| Acetone | 67-64-1 | C3H6O | 58.08 | 56.2 | -94.3 | 0.786 | Miscible | 20.7(25) | -18 |
| Acetonitrile | 75-05-8 | C2H3N | 41.05 | 81.6 | -46 | 0.786 | Miscible | 37.5 | 6 |
| Ammonia solution | 7664-41-7 | H3N | 17.03 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
22.4 |
- |
| Benzene | 71-43-2 | C6H6 | 78.11 | 80.1 | 5.5 | 0.879 | 0.18 | 2.28 | -11 |
|
Benzonitrile |
100-47-0 | C7H5N | 103.12 |
191 |
-13 | 1.01 | Insoluble |
- |
71 |
| 1-Butanol | 71-36-3 | C4H10O | 74.12 | 117.6 | -89.5 | 0.81 | 6.3 | 17.8 | 35 |
| 2-Butanol | 78-92-2 | C4H10O | 74.12 | 98 | -115 | 0.808 | 15 | 15.8(25) | 26 |
|
Butyl Acetate |
123-86-4 | C6H12O2 | 116.16 |
124-126 |
-106 | 0.882 | 0.68 |
- |
22 |
| tert-Butyl Alcohol | 75-65-0 | C4H10O | 74.12 | 82.2 | 25.5 | 0.786 | Miscible | 12.5 | 11 |
| tert-Butyl Methyl Ether | 1634-04-4 | C5H12O | 88.15 | 55.2 | -109 | 0.741 | 5.1 |
- |
-28 |
|
Carbon Disulfide |
75-15-0 | CS2 | 76.13 |
46 |
-110 | 1.2632 | 0.1185 |
- |
-30 |
| Carbon Tetrachloride | 56-23-5 | CCl4 | 153.82 | 76.7 | -22.4 | 1.594 | 0.08 | 2.24 | - |
| Chlorobenzene | 108-90-7 | C6H5Cl | 112.56 | 131.7 | -45.6 | 1.1066 | 0.05 | 2.71 | 29 |
|
1-Chlorobutane |
109-69-3 | C4H9Cl | 92.57 |
77-78 |
-123.1 | 0.886 | 0.07 |
- |
-6 |
| Chloroform | 67-66-3 | CHCl3 | 119.38 | 61.7 | -63.7 | 1.498 | 0.795 | 4.81 |
- |
| Cyclohexane | 110-82-7 | C6H12 | 84.16 | 80.7 | 6.6 | 0.779 | <0.1 | 2.02 | -20 |
| Deuterium oxide | 7789-20-0 | D2O | 20.03 | 101.3 | 4 | 1.107 | Miscible |
- |
- |
|
1,2-Dichlorobenzene |
95-50-1 | C6H4Cl2 | 147.00 |
180 |
-15 | 1.306 | Insoluble |
9.93(25) |
67 |
| 1,2-Dichloroethane | 107-06-2 | C2H4Cl2 | 98.96 | 83.5 | -35.3 | 1.245 | 0.861 | 10.42 | 13 |
| Diethyl Amine | 109-89-7 | C4H11N | 73.14 | 55.5 | -50 | 0.7074 | Miscible | 3.6 | -39 |
| Diethyl Ether | 60-29-7 | C4H10O | 74.12 | 34.6 | -116.3 | 0.713 | 7.5 | 4.34 | -45 |
| Diethyl Ketone | 96-22-0 | C5H10O | 86.13 |
102 |
-39 | 0.814 | 4.70 |
- |
13 |
| Diethylene Glycol Dimethyl Ether | 111-96-6 | C6H14O3 | 134.17 | 162 | -68 | 0.943 | Miscible | 7.23 | 67 |
| Diethylene Glycol | 111-46-6 | C4H10O3 | 106.12 | 245 | -10 | 1.118 | 10 | 31.7 | 143 |
| Dimethyl Sulfoxide | 67-68-5 | C2H6OS | 78.13 | 189 | 18.4 | 1.092 | 25.3 | 47 | 95 |
|
N,N-Dimethylacetamide |
127-19-5 | C4H9NO | 87.12 |
166 |
-20 | 0.937 | Miscible |
37.80 | 66 |
| Dimethylether | 115-10-6 | C2H6O | 46.07 | -22 | -138.5 |
- |
- |
- |
-41 |
| N,N-Dimethylformamide | 68-12-2 | C3H7NO | 73.09 | 153 | -61 | 0.944 | Miscible | 36.7 | 58 |
| 1,4-Dioxane | 123-91-1 | C4H8O2 | 88.11 | 101.1 | 11.8 | 1.033 | Miscible | 2.21(25) | 12 |
| Ethanol | 64-17-5 | C2H6O | 46.07 | 78.5 | -114.1 | 0.789 | Miscible | 24.6 | 13 |
|
2-Ethoxyethyl Ether |
112-36-7 | C8H18O3 | 162.23 |
180-190 |
-44 | 0.909 | ≥10 |
- |
82 |
| Ethyl Acetate | 141-78-6 | C4H8O2 | 88.11 | 77 | -83.6 | 0.895 | 8.7 | 6(25) | -4 |
|
Ethylene Glycol Dimethyl Ether |
110-71-4 | C4H10O2 | 90.12 | 85 | -58 | 0.868 | Miscible | 7.2 | -6 |
| Ethylene Glycol | 107-21-1 | C2H6O2 | 62.07 | 195 | -13 | 1.115 | Miscible | 37.7 | 111 |
| Formic Acid | 64-18-6 | CH2O2 | 46.03 | 100 | 8.3 | 1.21 | Miscible | 58.5 |
|
| Glycerin | 56-81-5 | C3H8O3 | 92.09 | 290 | 17.8 | 1.261 | Miscible | 42.5 | 160 |
| heptane | 142-82-5 | C7H16 | 100.20 | 98 | -90.6 | 0.684 | 0.01 | 1.92 | -4 |
| Hexamethylphosphor amide | 680-31-9 | C6H18N3OP | 179.20 | 232.5 | 7.2 | 1.03 | Miscible | 31.3 | 105 |
| Hexamethylphosphorous triamide | 1608-26-0 | C6H18N3P | 163.20 | 150 | -44 | 0.898 | Miscible |
- |
26 |
| Hexane | 110-54-3 | C6H14 | 86.18 | 69 | -95 | 0.659 | 0.014 | 1.89 | -22 |
|
Isoamyl alcohol |
123-51-3 | C5H12O | 88.15 |
130 |
-117 | 0.809 | 54 |
- |
43 |
|
Isobutyl alcohol |
78-83-1 | 78-83-1 | 74.12 |
108 |
-108 | 0.802 | 9.5 |
15.8(25) |
28 |
| Isopropanol | 67-63-0 | C3H8O | 88.15 | 82.4 | -88.5 | 0.785 | Miscible | 18.3(25) | 12 |
| Methanol | 67-56-1 | CH4O | 32.04 | 64.6 | -98 | 0.791 | Miscible | 32.6(25) | 12 |
|
2-Methoxyethanol |
109-86-4 | C3H8O2 | 76.10 |
124-125 |
-85.1 | 0.965 | Miscible |
16.90 | 38 |
|
2-Methoxyethyl Acetate |
110-49-6 | C5H10O3 | 118.13 |
145 |
-65 | 1.009 | Miscible |
- | 44 |
|
Methyl Ethyl Ketone |
78-93-3 | C4H8O | 72.11 | 79.6 | -86.3 | 0.805 | 25.6 | 18.5 | -7 |
|
Methyl Isobutyl Ketone |
108-10-1 | C6H12O | 100.16 |
117-118 |
-80 | 0.7978 | 1.9 |
- | 14 |
| 1-Methyl-2-pyrrolidinone | 872-50-4 | CH5H9NO | 99.13 | 202 | -24 | 1.033 | 10 | 32 | 91 |
| Methylene Chloride | 75-09-2 | CH2Cl2 | 84.93 | 39.8 | -96.7 | 1.326 | 1.32 | 9.08 | 1.6 |
| Nitromethane | 75-52-5 | CH3NO2 | 61.04 | 101.2 | -29 | 1.382 | 9.50 | 35.9 | 35 |
| 1-Octanol | 111-87-5 | C8H18O | 130.23 |
196 |
-15 | 0.826 | Insoluble |
- |
81 |
| Pentane | 109-66-0 | C5H12 | 72.15 | 36.1 | -129.7 | 0.626 | 0.04 | 1.84 | -49 |
| Petroleum ether | 8032-32-4 |
- |
- |
30-60 | -40 | 0.656 |
- |
- |
-30 |
| Propanoic acid | 79-09-4 | C3H6O2 | 74.08 | 141 | -21.5 | 0.993 | 37 | 3.4 | 51 |
| 1-Propanol | 71-23-8 | C3H8O | 88.15 | 97 | -126 | 0.803 | Miscible | 20.1(25) | 15 |
|
Propylene carbonate |
108-32-7 | C4H6O3 | 102.09 |
240 |
-55 | 1.21 | Moderately Soluble |
- |
132 |
| Pyridine | 110-86-1 | C5H5N | 79.10 | 115.2 | -41.6 | 0.982 | Miscible | 12.3(25) | 17 |
|
Tetrachloroethylene |
127-18-4 | C2Cl4 | 165.83 |
121 |
-22 | 1.623 | 0.015 |
- |
- |
| Tetrahydrofuran | 109-99-9 | C4H8O | 72.11 | 66 | -108.4 | 0.886 | 30 | 7.6 | -21 |
| Toluene | 108-88-3 | C7H8 | 92.14 | 110.6 | -93 | 0.867 | 0.05 | 2.38(25) | 4 |
|
1,1,2-Trichlorotrifluoroethane |
76-13-1 | C2Cl3F3 | 187.38 |
47-48 |
-36 | 1.575 | 0.02 |
- |
- |
| Triethyl amine | 121-44-8 | C6H15N | 101.19 | 88.9 | -114.7 | 0.728 | 0.02 | 2.4 | -11 |
| 2,2,2-Trifluoroethanol | 75-89-8 | C2H3F3O | 100.04 | 74.1 | -45 | 1.393 |
- |
26.5 |
29 |
| Water | 7732-18-5 | H2O | 18.02 | 100.00 | 0.00 | 0.998 |
- |
78.54 | - |
| m-Xylene | 108-38-3 | C8H10 | 106.17 | 139.1 | -47.8 | 0.868 | Insoluble | 2.37 | 27 |
| o-Xylene | 95-47-6 | C8H10 | 106.17 | 144 | -25.2 | 0.897 | Insoluble | 2.57 | 32 |
| p-Xylene | 106-42-3 | C8H10 | 106.17 | 138.4 | 13.3 | 0.861 | Insoluble | 2.27 | 27 |